What's new
Editor's pick
Research Article
Experimental study and comparative analysis of pitting fault in spur gear system
By Kemajou Herbert Yakeu Happi, Bernard Xavier Tchomeni Kouejou, Alfayo Anyika Alugongo
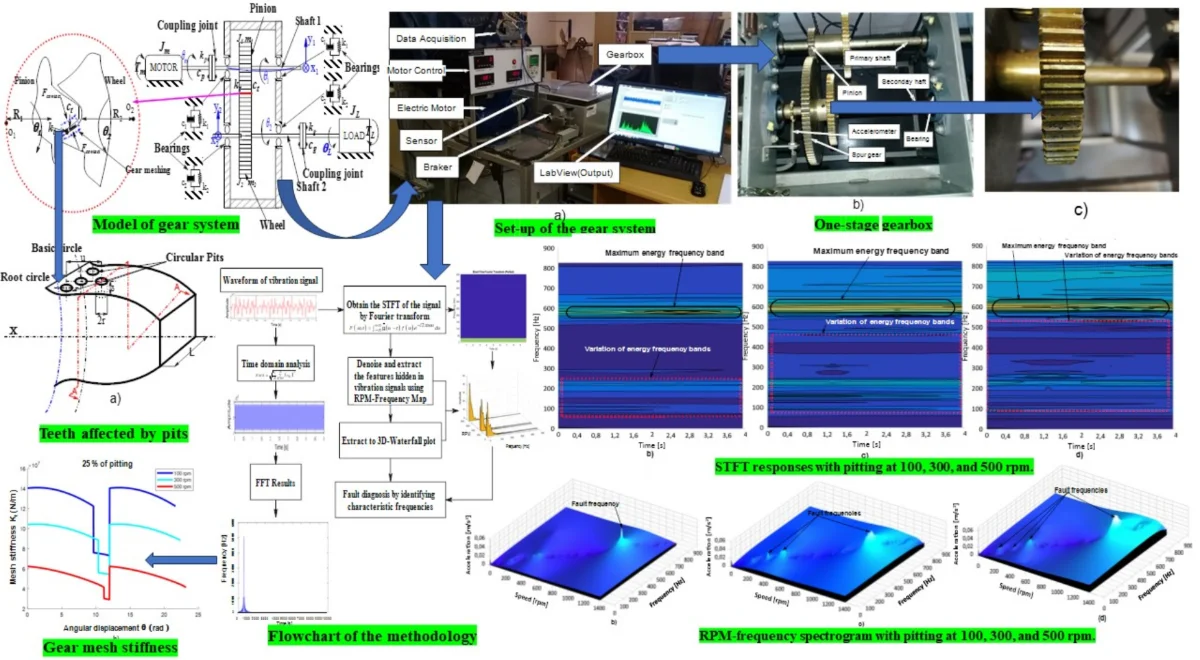
This paper uses a dynamic six-degree-of-freedom model that considers torsional and lateral motions to predict the impact of pitting on vibration parameters in a spur gearbox for various operating speeds and torque loads. The study examines the dynamic characteristics of a gearbox with localized pitting damage on a single gear tooth using theoretical and experimental approaches. The research analyzes the forced vibrations of a single-stage spur gear system with pitting damage, which includes variations in mesh stiffness, damping, and gear error excitation, to identify symptoms of default. The equation of motion for the rotary gearbox system is established using the Lagrangian method in tandem with Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) and frequency-RPM map fault diagnosis. During real-time vibration monitoring, vibration signals are captured via accelerometers and processed in both the time and frequency domains using the LabVIEW data acquisition signal processing package to extract diagnostic information. The experimental findings demonstrate how vibration analysis combined with time-frequency processing can recognize machine conditions even in harsh operational conditions. Moreover, the experimental results indicate a significant similarity with the theoretical analysis and validate the effectiveness of the RPM frequency technique-based pitting detection method, which can be an asset in gear fault monitoring.
September 14, 2023
Vibration Engineering
Research Article
Research on citrus segmentation algorithm based on complex environment
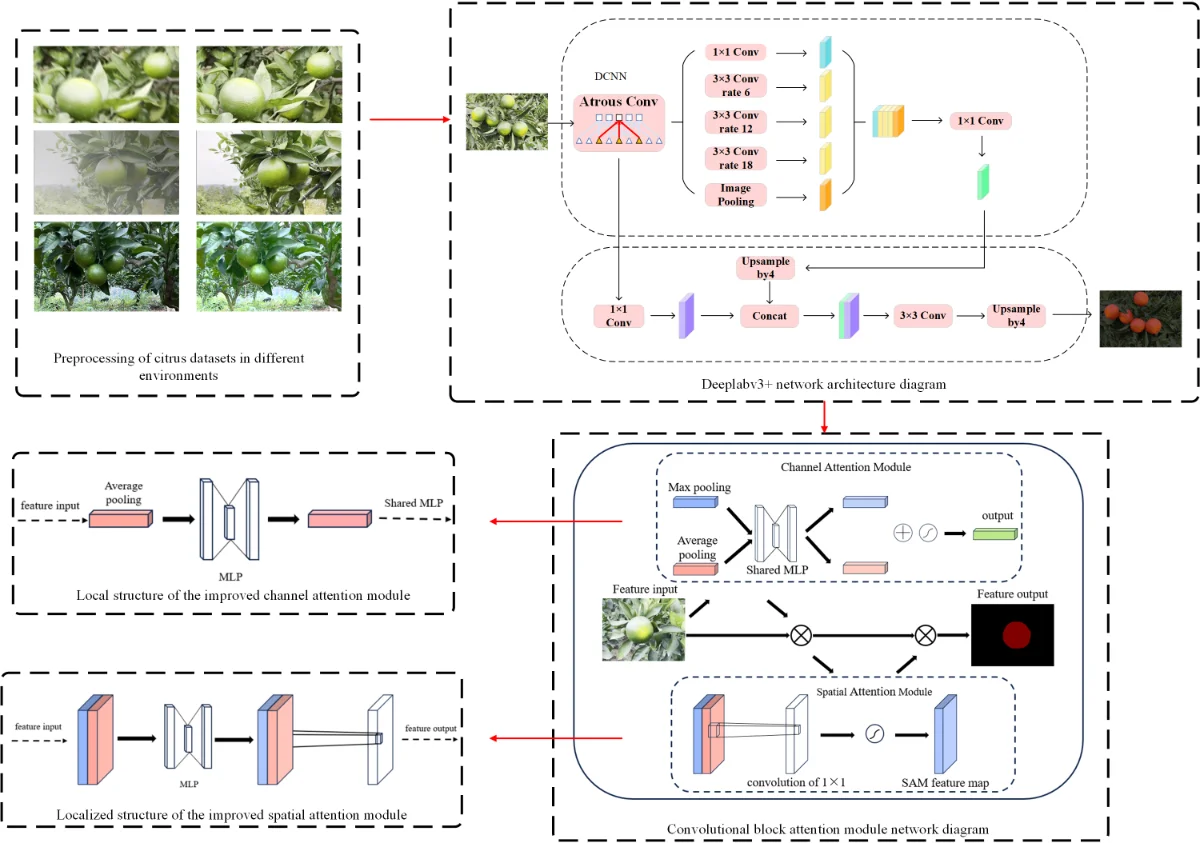
Aiming to address the low efficiency of current deep learning algorithms for segmenting citrus in complex environments, this paper proposes a study on citrus segmentation algorithms based on a multi-scale attention mechanism. The DeepLab V3+ network model was utilized as the primary framework and enhanced to suit the characteristics of the citrus dataset. In this paper, we will introduce a more sophisticated multi-scale attention mechanism to enhance the neural network’s capacity to perceive information at different scales, thus improving the model’s performance in handling complex scenes and multi-scale objects. The DeepLab V3+ network addresses the challenges of low segmentation accuracy and inadequate refinement of segmentation edges when segmenting citrus in complex scenes, and the experimental results demonstrate that the improved algorithm in this paper achieves 96.8 % in the performance index of MioU and 98.4 % in the performance index of MPA, which improves the segmentation effectiveness to a significant degree.
April 21, 2024
Informatics
Research Article
Methods of detection and localization of the sources of noise and vibration on car gearboxes: a review
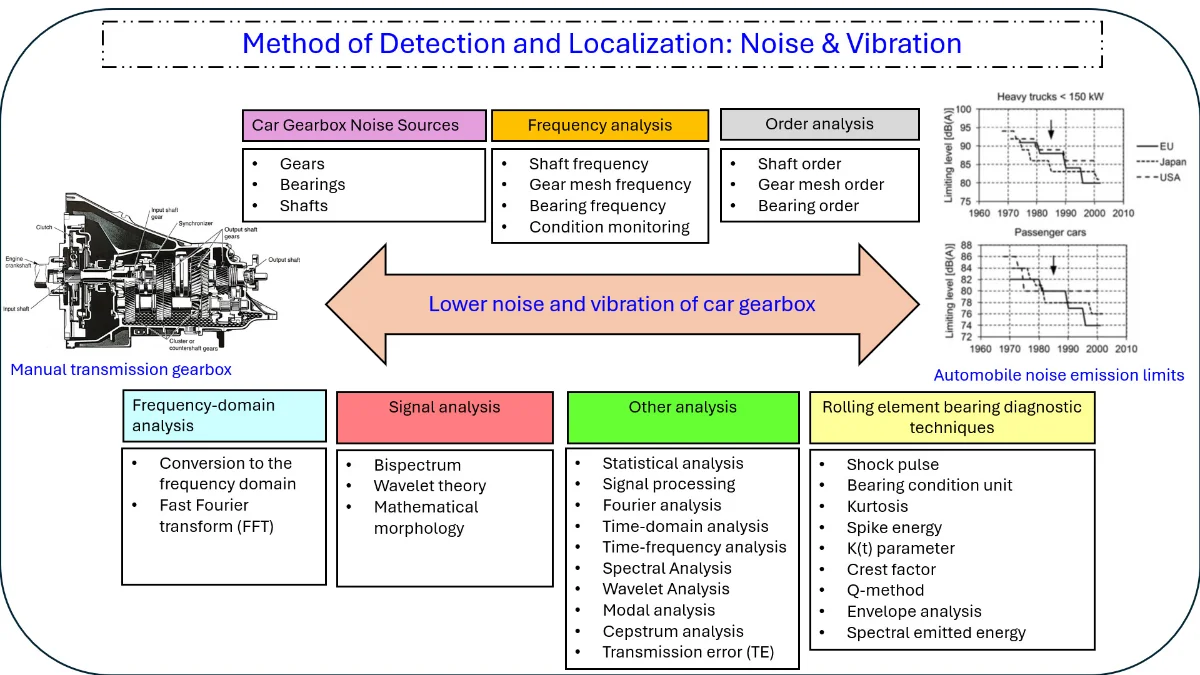
One of the primary sources of noise and vibration in automobiles is gearboxes. Shafts, gears, and bearings are the main causes of noise and vibration in vehicle gearboxes. Various studies have reported that vibrations’ root cause is bearing excitation. Besides bearing fatal defects or extreme structure resonance amplification, gear mesh is the primary source of high-frequency vibration and noise, even in newly built units. Gear damage detection is frequently crucial in automotive gearboxes and vehicle safety. Furthermore, vibrations caused by shaft imbalances, shaft misalignments, and other factors can cause noise and vibrations in the drivetrain's transfer path. In addition, the vibration of an automobile gearbox is closely related to poor design, construction quality, and production accuracy. This paper reviewed previous research and methods on car gearboxes for conventional vehicles. It was obvious that frequency analysis and order analysis were commonly used in noise and vibration analysis on car gearboxes. Envelope analysis is usually used to analyze bearing faults. Finally, rolling-element bearing diagnostic techniques were also reviewed.
April 14, 2024
Applied Mathematics
Research Article
A lift stopping mechanism controlled by a special rope fastening
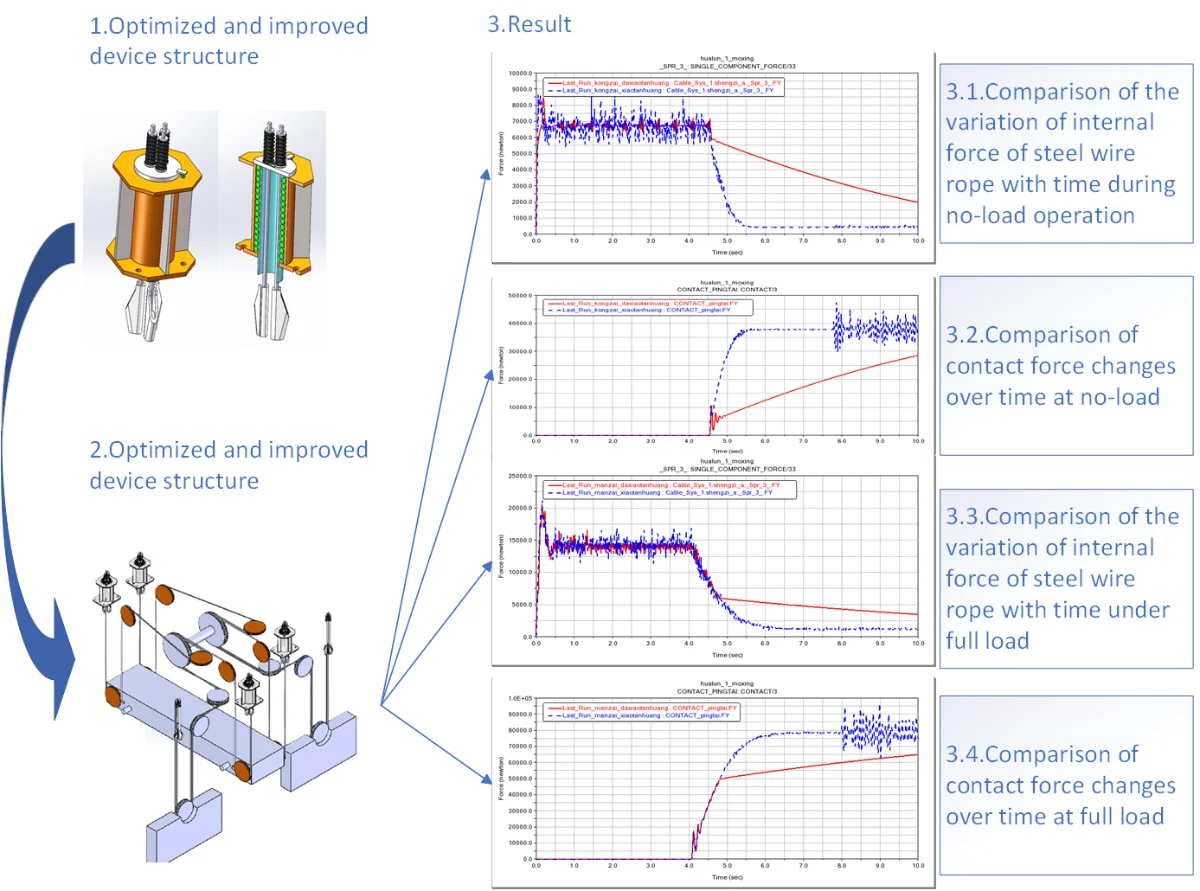
The lift leveling mechanism provided in this paper is controlled by the special rope fastening. By using the lift leveling mode controlled by the rope fastening, the leveling mode of the lifting system can be changed to the braking stop of the drive system after the platform is lowered and placed on the bracket. The problem of anchorage precision and the vibration caused by elastic expansion of the rope during platform loading and unloading are effectively solved by using the supporting function of the piers. In the process of studying this problem, we simplified a heavy-duty elevator system to form a simplified model that can be used for simulation research. The device provided in this article provides a new solution for the leveling of the heavy-duty lifting system, which not only ensures the leveling accuracy of the lifting platform during loading and unloading, but also effectively reduces the impact during leveling, which has a beneficial guiding effect on this type of equipment.
April 4, 2024
Vibration Engineering

Research Article
Analysis of vibration response characteristics of composite pipeline based on finite element method
In order to ensure the good stability of the composite pipeline under fluid dynamic loads, finite element analysis method was applied to simulate and calculate the modal characteristics under dry and wet mode conditions. According to the working principle and structural characteristics of composite pipelines, the model was parameterized and simplified to improve computational efficiency and convergence. The modal testing platform is constructed, consisting of a combination of pipeline structure and pipeline support structure. The movement direction of the slider is limited by the guide rail used, allowing the horizontal section of the branch to move only along its own pipeline axis direction. The fluid structure coupling analysis technology was applied to obtain the vibration mode and spectral response results of the composite pipeline, which was verified through an experimental platform. The research results indicate that the natural frequency in wet mode was about 16 % lower than that in dry mode. In addition, it could be proven that the simulation scheme had good computational accuracy, with a maximum error of 9.2 %.
April 4, 2024
Vibration Engineering
Latest from engineering

Research Article
Modal and fatigue characteristics analysis of key components of tower crane
In order to ensure good stability and safety of the tower crane under long-term heavy load conditions, modal analysis and fatigue analysis were conducted on its key components, including standard section and frame section. The connection points of each truss structure were regarded as indivisible common nodes, and the model was simplified and parameterized, resulting in improved mesh quality and computational efficiency. Based on Pro/E, standard section and frame section models were established and imported into Workbench through intermediate data formats for simulation calculations in modal and static structural modules. By calculation, the natural frequency and modal shape of the standard section, as well as the lifespan, damage, and safety factor of the frame section, were obtained. It can be seen that the standard section has good structural stability and can maintain relative balance under excitation in different directions and degrees of freedom. If the safety factor of the web components is high and the service life is improved from a structural perspective, it can be considered to increase the thickness of the chord members.
April 4, 2024
Vibration Engineering
Research Article
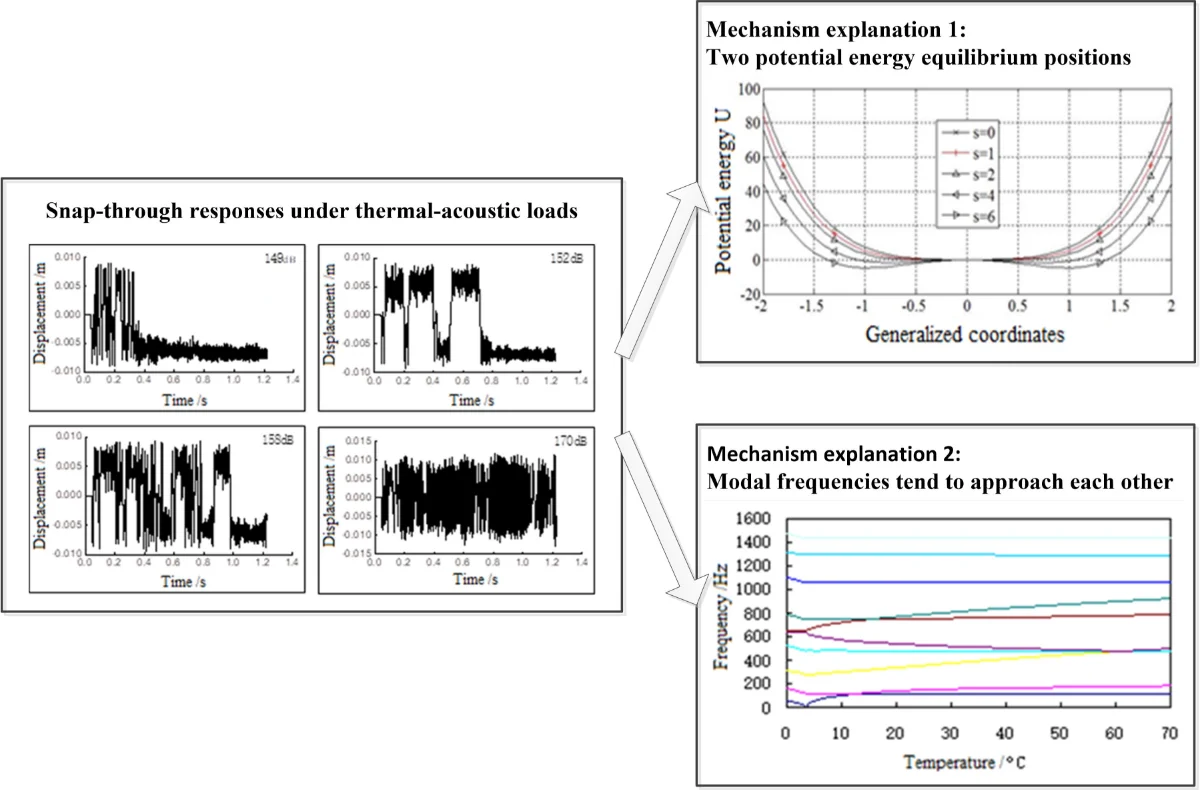
Acoustic vibration analysis of high-temperature thin-walled structures
Advanced aerospace structures are subjected to extremely harsh working environment, including of mechanical, acoustic, thermal, and aerodynamic loads. These combined loads can make the structures exhibit complex response, which has already attracted increasing concern in the design of advanced aerospace structures. To tackle the problem, a finite element model (FEM) by discretizing the theoretical differential equation is established to calculate the dynamic response of thin-walled structures under combined thermal and acoustic loads. The numerical analysis indicates that three types of nonlinear responses of the thin plate under combined thermal-acoustic loads are obtained, and the mechanism of snap-through is revealed through two ways: thermal buckling analysis and thermal modal analysis. which can be used to explain the nonlinear response characteristics.
April 4, 2024
Public Health
Research Article
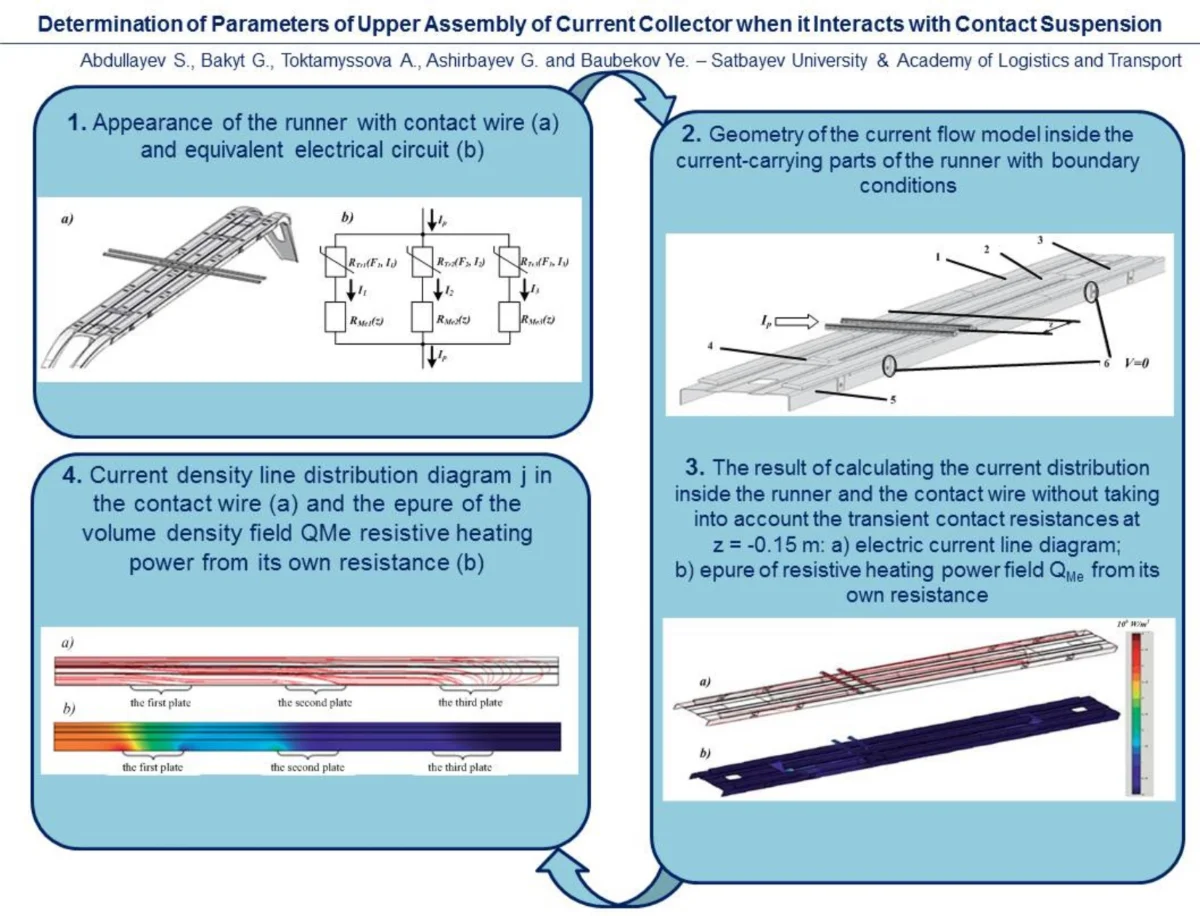
Determination of parameters of upper assembly of current collector when it interacts with contact suspension
In this article, the definition of the current density field at current collection was reduced only to the calculation of the thermal (resistive) action of the electric current. These procedures must include consideration of the bending stiffness of the contact wires to calculate the distribution of the pressing force on the contact wire between the current collecting plates. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the existing methods for calculating the dynamics of mechanical interaction of the current collector with the chain suspension. As a result of computer modeling in the Comsol Multiphysics software package, the volumetric power density of resistive heating from the intrinsic resistance of the contact wire was determined.
April 4, 2024
Informatics
Research Article
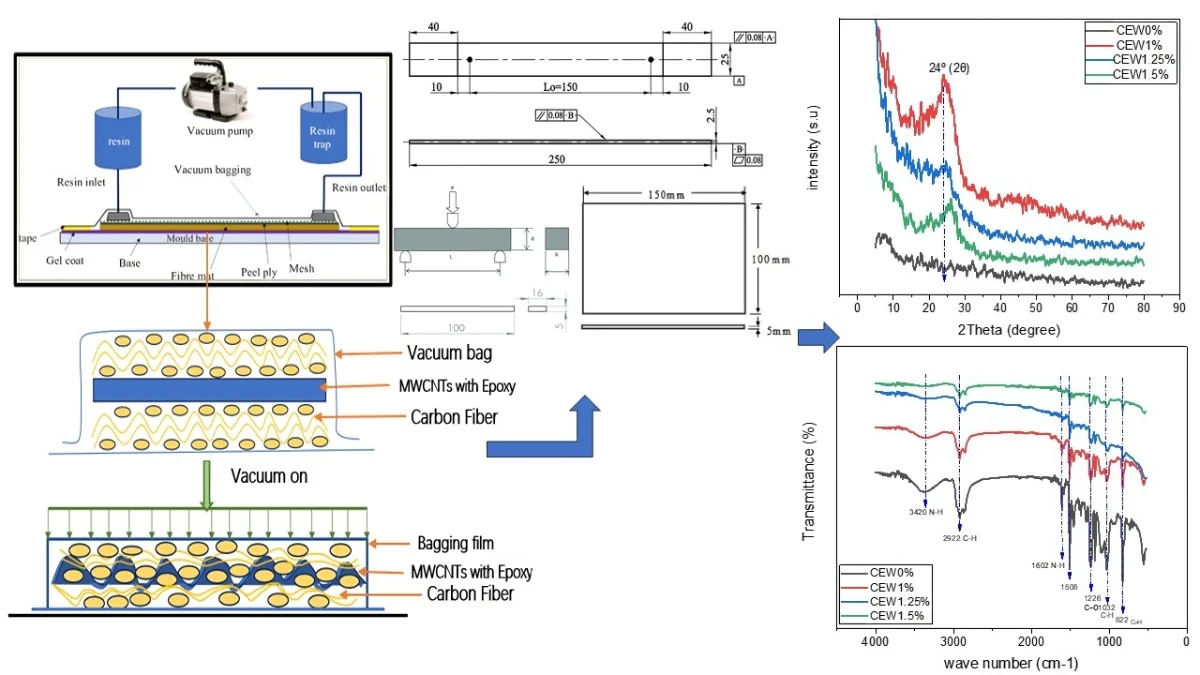
Investigation of fracture behavior and mechanical properties of epoxy composites supported with MWCNTs microscopically
Adding of a multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) to epoxy resin has shown promising results in improving fracture toughness in bulk epoxy and carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy composites (CFRP). using a hand layup proceeding followed by the so called vacuum bagging process method, carbon fiber-reinforced polymer multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) was added to an epoxy resin with a weight percentage mixing of 1% wt., 1.25% wt., and 1.5 % wt. MWCNTs. Furthermore, the specimen underwent analysis via Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and X-ray Diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy, the composites were subjected to a microscopic examination using a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). FTIR and XRD verified the folding and unfolding of the polymer, in addition, the mechanical properties including tensile strength, bending stress, and impact behavior were investigated as well as the hardness test. The obtained results showed a significant improvement of about (40 %) in tensile strength, (53 %) in bending stress at 1 % wt. MWCNTs, and (70 %) percentage increment in the strength of Impact at 1.25 % wt. MWCNTs. And the gained hardness was about 40.5 HV which were compared with a reference substance named Carbon Fiber (CF) without any addition of nano materials. Carbon nanotubes have demonstrated their potential to enhance the mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced polymers, so this investigative study employs comprehensive characterization techniques, and demonstrates significant improvements in mechanical properties for the modified polymeric composite materials supported with nano materials.
April 4, 2024
Applied Physics
Recently published
Research article
April 4, 2024
Cavitation fault diagnosis of centrifugal pump based on RIME-SDAE
By Honghui Song, Hui Sun, Ning Chen
Recently published
Research article
March 2, 2024
Testing the effect of functional orthopedic appliance Simões network 6 (SN6) through surface electromyography on rest mandibular position – a pilot study
By Sergio Polízio Terçarolli, Eduardo Sakai, Orlando Santiago Jr, Michelly Marin P. Sutti, Stella Travalão Faria Dumke, Murilo Bovi Corsi
71st International Conference on VIBROENGINEERING
Major Conference Topic: Vibration & Condition Monitoring Problems
Date
December 12-13, 2024
Submission deadline
November 4, 2024
Conference format
Hybrid
Best of engineering
Editor's pick
Research article
April 4, 2024
Analysis of regulative documents in the field of human vibration safety
By Tsygankov Sergey, Abdreshov Shamil, Imangaliyeva Aizhan, Bimagambetova Lalita, Kurmashev Baurzhan, Torgayev Abish
Editor's pick
Research article
March 2, 2024
A simple harmonic quantum oscillator: fractionalization and solution
By Iqbal M. Batiha, Iqbal H. Jebril, Abeer A. Al-Nana, Shameseddin Alshorm
Editor's pick
Research article
February 14, 2024
An improved stochastic averaging process on a monostable piezoelectric vibrational energy harvester model excited by colored noise
By Bo Li, Yusen Li, Gen Ge
Editor's pick
Research article
November 27, 2023
Timber-to-timber composite floors connection optimization for vibration and deflection reduction
By Yuri De Santis, Francesca Pancella, Dag Pasquale Pasca, Angelo Aloisio, Massimo Fragiacomo
You might also like
Most downloaded
Research Article
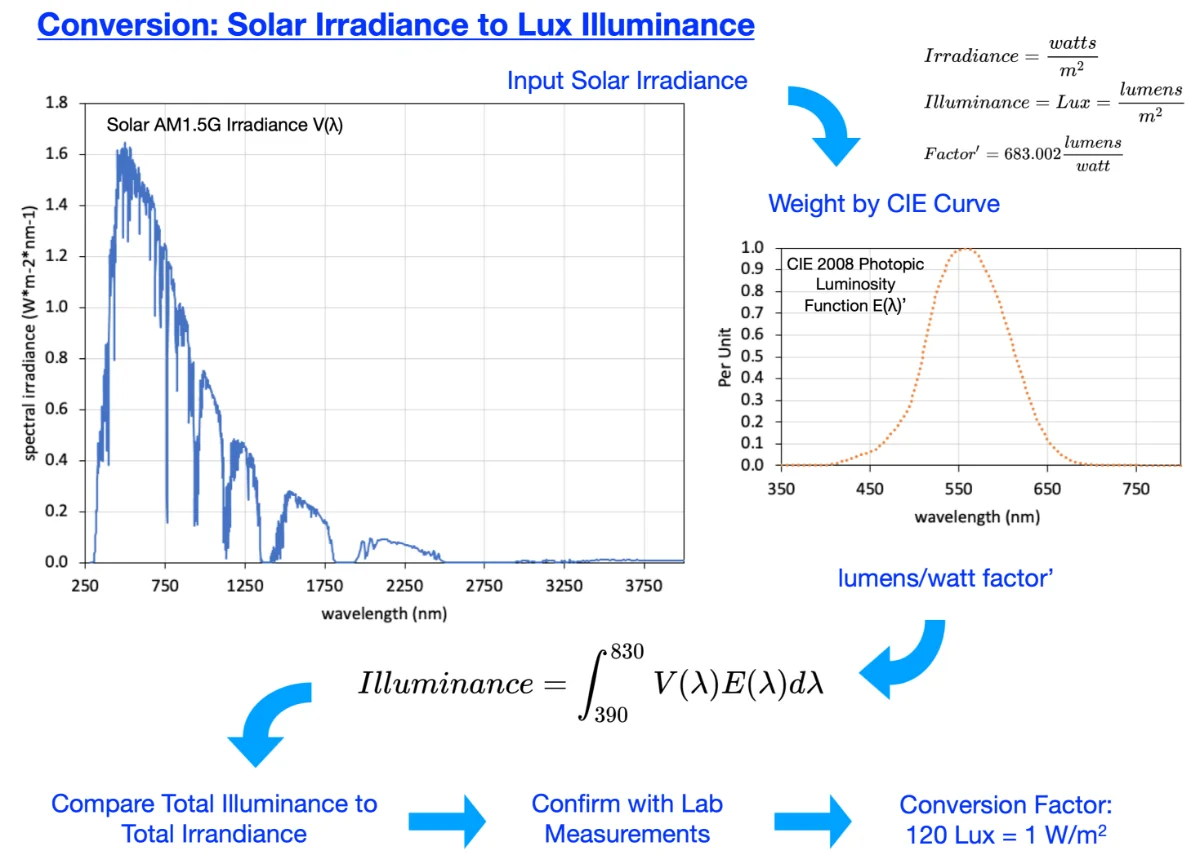
A conversion guide: solar irradiance and lux illuminance
By Peter R. Michael, Danvers E. Johnston, Wilfrido Moreno
The standard for measuring solar irradiance utilizes the units of watts per meter squared (W/m2). Irradiance meters are both costly and limited in the ability to measure low irradiance values. With a lower cost and higher sensitivity in low light conditions, light meters measure luminous flux per unit area (illuminance) utilizing the units of lumens per meter squared or lux (lx). An effective conversion factor between W/m2 and lx would enable the use of light meters to evaluate photovoltaic performance under low solar irradiance conditions. A survey of the literature found no definitive and readily available “rule of thumb” conversion standard between solar irradiance and illuminance. Easy-to-find Internet sources contain conflicting and widely varying values ranging from 688449 to 21000 lx for 1000 W/m2 (1 Sun) of solar irradiance. Peer-reviewed literature contains Luminous Efficacy equivalent values ranging from 21 to 131 lx per W/m2. This manuscript explores the relationship and establishes a theoretical and laboratory measurement guide for the conversion between solar irradiance and illuminance. The conversion factor includes standards data, equipment calibration accuracy, and uncertainty estimates. Solar Irradiance of 1 Sun (1000 W/m2) for an LED-based solar simulator is (116 ± 3) klx and (122 ± 1) klx for outdoor sunlight.
December 4, 2020
Applied Physics
Most downloaded
Research Article
Modal finite element analysis of PCBs and the role of material anisotropy
By Uday H. Kalyani, Mark Wylie
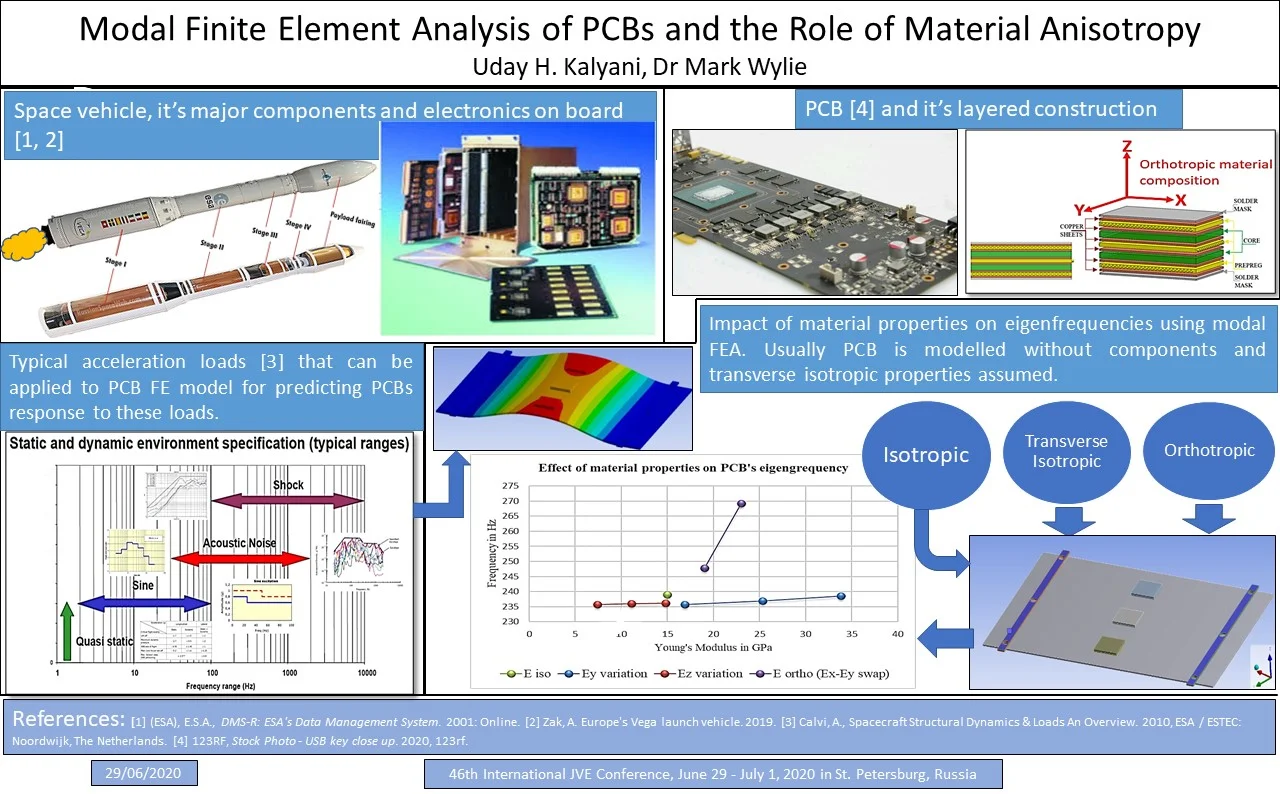
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are epoxy resin-impregnated and cured sheets of counter woven glass fabric (e.g. FR4) laminated between thin sheets of Copper. The nature of the PCB is inherently anisotropic and inhomogeneous but previous modal FEMs of PCBs have assumed isotropic, anisotropic (transversely isotropic and orthotropic) material properties and shown good correlation with test data for specific scenarios [1-3]. This paper details part of a research program aimed at gaining a better understanding of accurately modeling PCB’s dynamic behavior. New investigations into the impact of material anisotropy and, in particular, the effect of material orthogonal plane definition (Ex and Ey) on eigenfrequencies is analysed. A modal FEM of a JEDEC PCB is created, verified, and validated using well established theories by Steinberg and empirical data by others [4, 5]. The relative contributions of Ex, Ey and Ez on PCB eigenfrequencies is examined using a parametric modal FEM, analysing the role of material isotropy verses anisotropy. The impact of transversely isotropic material properties is also analysed for a typical JEDEC PCB. This analysis details the mesh density required for accurately modeling the PCB eigenfrequencies. The results show that a 100 % increase in Ez has only a 0.2 % difference in the eigenfrequency where as a 100 % increase in Ey has a 1.2 % difference in the eigenfrequency. The effect of orthotropic plane definition (alternating Ex with Ey) on the JEDEC PCB amount to a 7.95 % delta in eigenfrequency.
June 29, 2020
Vibration Engineering
Design and calculation of double arm suspension of a car
Suspension system is one of the challenging portions in designing a vehicle. The complete stability of the vehicle under dynamic conditions depends on the suspension system of the vehicle. Suspension system of a vehicle is interlinked with other systems such as steering, Wheels and Brakes. The main objective of this document is to provide complete guidance in designing and calculation of an independent suspension system with double control arms. The required parameters are calculated on considering a prototype vehicle with gross weight of 350 kg such as required stiffness of shock absorbers, Ride frequency, Motion ratio, Coefficient of damping etc. A CADD model was made with CATIA v5 r20 and SOLIDWORKS on the basis of calculations obtained and stress analysis was carried out for this model in various software such as Ansys. The complete assembled model was tested in LOTUS Shark and the result was obtained.
Coilgun design and evaluation without capacitor
Capacitors with high voltage and capacity values are used in most induction coilguns that are designed and constructed. The fact that capacitors are quite bulky and slow in energy transfer and how a coilgun can be made without using capacitors is the study subject of this article. Two and four coil gun samples were made to find the essential components of an electric gun, and the results are reported in this article. The accuracy of the results is also confirmed by FEMM analysis for these models. The harmony of experimental and theoretical results shows that smaller and low cost portable electrical weapons can be a powerful alternative to firearms in the future.